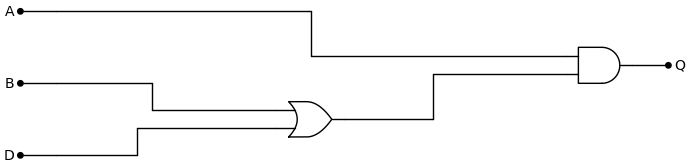
GateBench is a challenging benchmark for Vision Language Models (VLMs) designed to test visual reasoning and image understanding capabilities. The benchmark requires VLMs to extract boolean algebra expressions from images of logic gate circuits, using this task as a proxy for assessing detailed image understanding and complex visual reasoning.
| Model | Score |
|---|---|
| gemini-3-pro-preview (high) | 53.1% |
| gpt-5.1 (high) | 40.6% |
| qwen3-vl-235b-a22b-thinking | 39.0% |
| qwen3-vl-235b-a22b-instruct | 32.8% |
| gemini-2.5-flash | 32.8% |
| qwen3-vl-30b-a3b-thinking | 20.3% |
| qwen3-vl-30b-a3b-instruct | 15.6% |
| claude-opus-4.5 (non-thinking) | 15.6% |
| glm-4.5v | 15.6% |
| llama-4-maverick | 15.6% |
| claude-sonnet-4.5 (thinking) | 14.1% |
| claude-opus-4.5 (thinking) | 14.0% |
| nova-2-lite-v1 (thinking) | 9.4% |
| llama-4-scout | 7.8% |
| nova-2-lite-v1 (non-thinking) | 6.3% |
| claude-haiku-4.5 | 6.2% |
| grok-4.1-fast | 4.6% |
| claude-sonnet-4.5 (non-thinking) | 3.1% |
| mistral-large-2512 | 0.0% |
Unlike benchmarks that focus on single-object recognition (e.g. Name the breed of the dog in the image), GateBench is difficult because it requires the model to reason over the entire image. The model must correctly identify multiple logic gates, trace the connections between them (wires), and understand the logical flow to derive the correct boolean expression.
Key capabilities tested:
- Visual Reasoning: Tracing complex connections and data flow in a diagram.
- Image Understanding: Identifying specific symbols (logic gates) and their spatial relationships.
- Symbolic Translation: Converting visual diagrams into structured text (boolean expressions).
User:
Extract the boolean algebra expression from the image.
Respond with the single line boolean algebra expression in a code block. Use operators in word form, not symbols. (e.g. "and" instead of "∧")
Example:
not ((A and B) xor C)
- Challenging Test Suite: Includes diagrams of varying complexity (different gate counts).
- Multi-model Support: Compatible with OpenAI-compatible APIs (OpenAI, OpenRouter, etc.).
- Automated Evaluation: Automatically verifies the equivalence of the extracted expression against the ground truth using boolean algebra rules.
- Caching: Caches model responses to avoid redundant API calls and costs.
- Python 3
pip
git clone https://github.com/johnbean393/GateBench.git
cd GateBenchpip install -r requirements.txtThe main entry point for the benchmark is src/run.py.
Run the benchmark on a specific model using an OpenAI-compatible endpoint (defaults to OpenRouter):
python src/run.py --model "openai/gpt-4o" --api-key "your-api-key"--model: The model identifier (e.g.,openai/gpt-5.1,anthropic/claude-sonnet-4.5). You can test multiple models by separating them with a semicolon (e.g.,"model1;model2").--api-key: Your API key for the endpoint.--endpoint: The API endpoint URL (default:https://openrouter.ai/api/v1).--open-router-api-key: Specific API key for OpenRouter if different.--reasoning-effort: Set reasoning effort (high, medium, low) for models that support it.--reasoning-max-tokens: Max tokens for reasoning (for models like Claude that support thinking/reasoning parameters).
Run with OpenRouter:
python src/run.py --model "anthropic/claude-sonnet-4.5" --api-key "sk-or-..."Run multiple models:
python src/run.py --model "google/gemini-3-pro-preview;openai/gpt-5.1" --api-key "sk-..."GateBench/
├── cache/ # Cached model responses
├── questions/ # Dataset files
│ ├── expressions.json # Ground truth expressions
│ └── images/ # Generated logic gate diagrams
├── results/ # Benchmark results
├── src/ # Source code
│ ├── run.py # Main execution script
│ ├── llm.py # LLM interface handler
│ ├── expression_evaluator.py # Evaluation logic
│ └── diagram_renderer.py # Logic gate diagram generator
└── requirements.txt # Python dependencies
The benchmark evaluates the model's accuracy by comparing the extracted boolean expression with the ground truth. Since equivalent boolean expressions can be written in multiple ways (e.g., De Morgan's laws), the evaluator checks for logical equivalence rather than simple string matching.